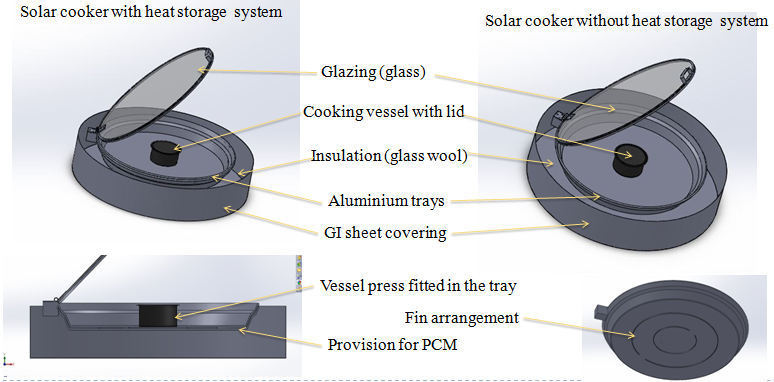
Two solar cookers one without thermal storage system and other one with thermal storage system with identical dimensions are to be designed and fabricated. This design consists of aluminium trays and cooking vessels to cook the food, Paraffin wax is used as the thermal storage system(phase change material), glass wool for insulation, metal sheet as the outer casing, Glass is used as a glazing surface to the cooker. Standard parts have been used for most of the components. The design is simple and made with materials that are easily available in the market.
DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS
Outer casing, side covering (GI sheet of thickness 0.2mm) and bottom plywood of thickness 12mm (Ø980mm);
Tray-inner cooker box, aluminium sheet of thickness 3 mm,(diameter 7800mm, Thermal conductivity(k) = 237 W/m-K, Emissivity = 0.9);
Glazing, ordinary glass sheet of 4 mm thickness, diameter 780mm;
Insulation-glass wool, 20 mm, Thermal Conductivity (k) = 0.04 W/m-K;
Cooking pot, aluminium cylinder, diameter = 300 mm, height = 80 mm, with dull black paint;
PCM, Paraffin wax, 3kgs.
Aperture area of π(780)^2 mm.
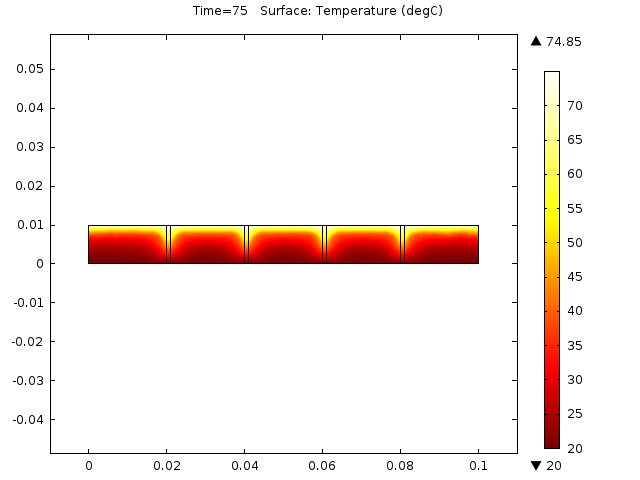
Results
Table 3: Experimental values of base temperature and water temperature at 30min time interval for with and without thermal storage system respectively
Heat Transfer Vs Time with fins
Heat Transfer Vs Time with out fins
Future work
There is always room for improvement. The whole cooker can be much optimized and redesigned to increase the efficenlt and decrese the cost.
Temperature gradient can be reduced in a solar cooker by incorporating PCM with high temperature ranges temperature falls down gradually in thermal storage solar cooker and the selected PCM should be cost effective and abundantly available.
Cost of the setup can be further reduced by using cotton as insulation material as it is cheaply available in rural India.
The outer casing can be replaced with bamboo baskets that can be weaved in houses.
Size of the cooker should be optimized by reducing the losses and by using tempered glass or double glazing.
Using reflectors can greatly increase the efficiency of the cooker.
Team
Sandeep Vempati